Artificial Intelligence: Tool for Genealogical Research
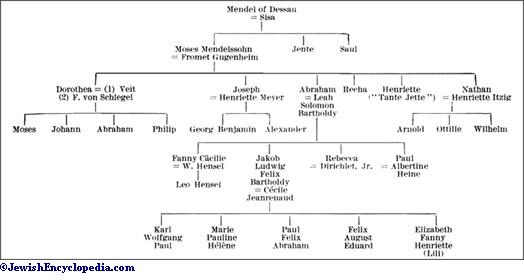
Courtesy https://picryl.com/amp/media/medelssohngenealogy-27a4b2 "AI for Genealogy" is a hot topic these days, but often it is discussed as if it's new. In fact, artificial intelligence (AI) has been used for all kinds of research for a long time. It all depends on how we "AI" define it. Remember, genealogy tree diagrams such as the above diagram were a revolution in how to think about and display family relationships. New: Chatbots Chatbot Courtesy VectorPortal.Com What's new is the chatbots such as ChatGPT. A recent article at ZDnet says, "Whether unlocking your phone through face recognition or telling Alexa to play a song, artificial intelligence has filtered into our everyday lives. Now, you can harness the power of AI to do your writing, too. At your command, AI chatbots can write that paper you have been dreading to start, write code, compose emails, generate art or even write Excel formulas for you. "ChatGPT has made quite a splash, moti...



